Let’s talk about AI in medical devices. Med tech companies have been using AI long before the advent of OpenAI and ChatGPT. Different forms of AI have been responsible for healthcare innovations like:
- Image analysis
- Robot-assisted surgery
- Forecasting disease progression
- Data management and analysis
- Assisted clinical trials
This is article number 3 in our AI and medical device series. Catch up on articles 1 and 2; here.
However, with the advent of OpenAi and ChatGPT we are looking at a future beyond that. With Open AI’s image recognition, pre-trained deep learning model, and Natural Language processing, we are looking at a future where it’s possible to:
1) drastically boost human productivity by automating repetitive tasks and creating systems specific to a project’s needs and team preferences. Check out the 7 ways GPT4 can help you save time.
2) expedite the discovery of new scientific breakthroughs by designing experiments, collecting and interpreting data, analyzing complex problems, and generating insights in half the time.
3) facilitate the human decision-making process by providing additional analyses and information
4) find hidden correlations in data, sometimes in real-time. For e.g. between symptoms and diagnoses or between a quality issue and the manufacturing process.
5) predict and prevent previously undetectable diseases and conditions. It can even give warnings and personalized treatment plans!
There are a few things to keep in mind before going ahead with AI in medical device manufacturing.
1) The OpenAI model is pre-trained. Meaning, the data sets (the information) it is trained on are limited, and at times outdated. So the results you get from it may not be actually useful. In some cases, they may cause harm. You can train your own GPT model, but that requires a significant amount of time and money.
2) To keep learning and training, open AI will (and does) build on conversations users had with it. That means it’s your data, your proprietary property, and your company information that is going into training AI. And as this information is not stored on your private company servers, the potential risk of leaks is high. Your proprietary information will not remain proprietary for long.
3) There’s also the ethical concern of patient safety. How does one protect their clinical trial results and patient information on an open-source platform? Can Institutional Review Boards, Data and Safety Monitoring Boards, and Observational Study Monitoring Boards even see how the patient data is being used in GPT?
Yes, AI can find correlations in data sets and identify patterns. But it’s not intelligent enough to tell which of those correlations are actually meaningful. Case in point🔽🔽
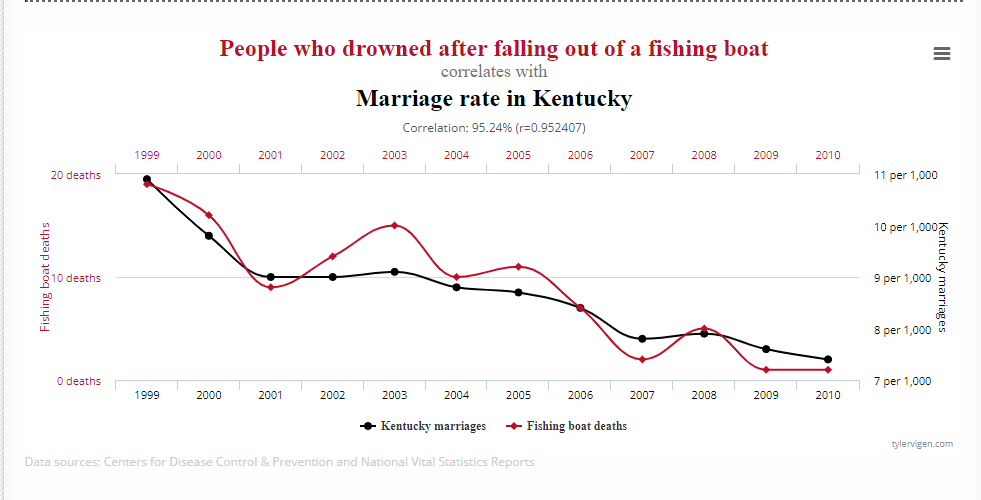
Apparently, there’s a correlation between people who drowned after falling out of a fishing boat and the marriage rate in Kentucky.
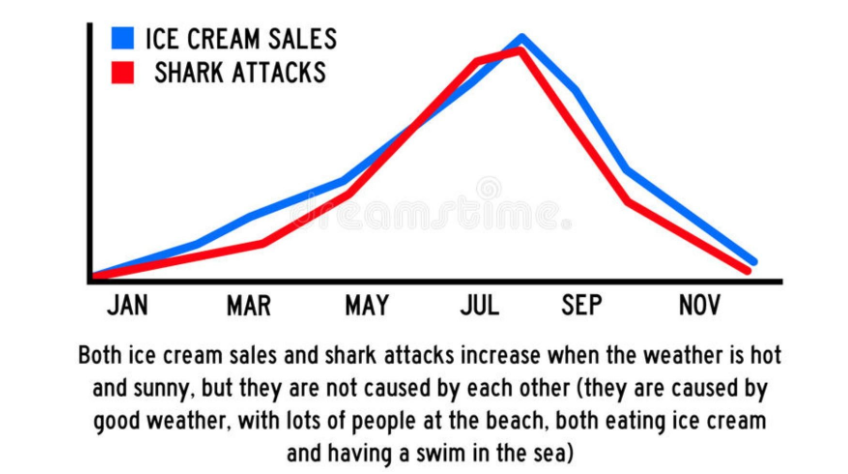
And if you’re still skeptical(😉) there’s also a correlation between ice-cream sales and shark attacks! But is it meaningful?
4) Despite the updates, OpenAI still hallucinates results and may give out false information not backed by real-world data. Something like this is drastically harmful to a high-stakes industry like medical devices. It can impact a company’s reputation and the success of current and future medical device projects.
5) Current deep learning models are trained with a gigantic amount of data created by humans (for example data on the internet, curated data, and literature). As a result, they unavoidably absorb a lot of flaws and biases that exist in our society. That’s not something you’d want to be associated with or have as a part of a controlled study.
For example, when DALL·E was asked to portray a nurse, it would only generate female characters, or for a professor, it would only generate white people. The model captures biases in real world statistics or biases in our training data. – Lilian Weng, Applied AI Research at OpenAI.
So can Open AI help you improve and revolutionize your medical device company? Yes. Should it? A hard no
An alternative can be using a closed-source AI model instead.
AI Closed source AI, involves proprietary technologies that are developed and controlled by specific companies or organizations. It offers advantages such as intellectual property protection and specialized support.
However, because it can’t ‘learn on the go,’ i.e. learn from publicly available data, it lacks the transparency and community-driven development found in open-source AI. It also requires a huge time and budget investment.
In the coming years, there is a possibility of using hybrid models that can overcome the individual limitations of each kind of AI model. But will they still be ethical and private? Only time will tell.
Are you interested in learning more about Artificial Intelligence in the Medical Device Space?
Waddell Group, in partnership with the Medical Device Resources Group, is hosting a symposium about Medical Device uses of AI September 27th from 4-6:30 PM at Surly Brewing. Attendance is free, but you must RSVP, which you may do here: Signup Here!